How PowerInfer‑2 Turns Your Smartphone Into an AI Workstation
Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
- Background and Motivation
- PowerInfer-2 Overview
- Neuron-Aware Runtime Inference
- Execution Plan Generation
- Implementation
- Evaluation
- Related Work
- Conclusion and References
5 Execution Plan Generation
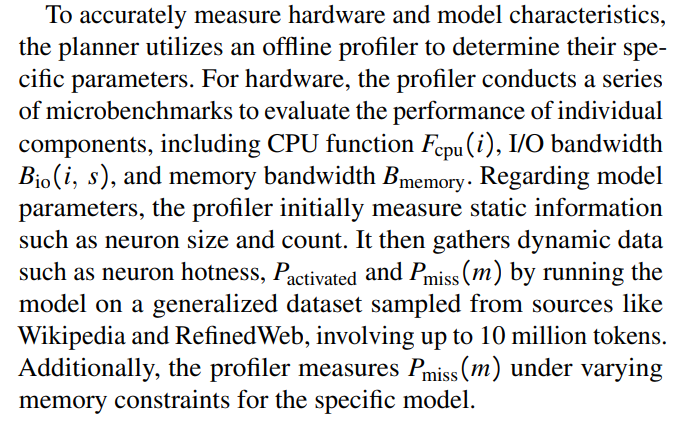
Today’s smartphones are equipped with a variety of hardware specifications, such as differing CPU capabilities, I/O throughput, and DRAM sizes. Users deploying LLMs on these devices also have diverse objectives. Some may prioritize a balance between generation speed and memory usage, while others aim to maximize hardware utilization for increased speed. Additionally, the models themselves vary in weight numbers, structures, and sparsity levels. To manage this complexity, PowerInfer-2 includes an offline planner specifically designed to develop execution plans that optimally meet these varied requirements.
\
5.1 Execution Plan
\
5.2 Input Parameters
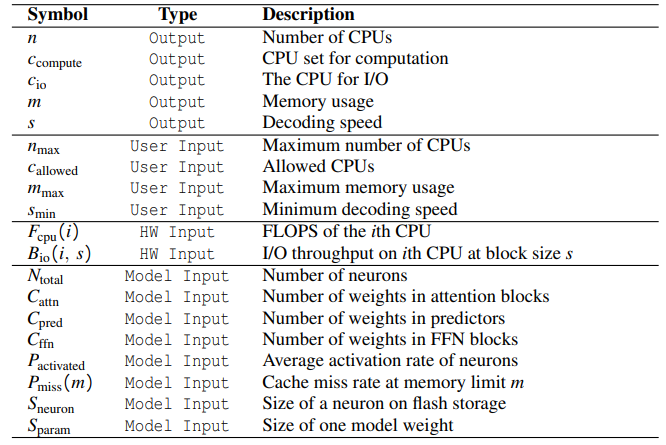
Table 2 also lists three categories of input parameters:
\ • Hardware: Parameters profiled from the hardware, such as CPU FLOPS, I/O throughput, and memory bandwidth.
\ • User: Parameters specified by the user, such as CPU constraints, memory limit, and lower bound of decoding speed.
\ • Model: Parameters about the model collected by an offline profiler, such as the size of the model, sparsity levels and caching characteristics, etc.
\ 
\
5.3 Cost Model
After collecting the input parameters, the planner uses a cost model to generate the execution plan. The goal is to maximize the generation speed s (as defined by Equation 1) while adhering to user-specified constraints (Formulas 3-5). The decoding speed s is inversely proportional to the time taken to decode one token (Equation 1), which is determined by the computation times for that token (Equation 2), as we efficiently overlap the computation and I/O operations. As we have defined the objective function and the constraints, the constructed model can be solved by mature SMT solvers. In our implementation, we utilize the Z3 solver [11] to solve the cost model.
\ 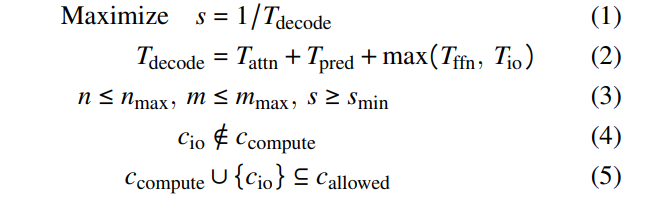
\ To compute the decoding time, we first model the times for computation. As we observed that memory opeartion is not a significant factor compared to the computation, we do not consider it in the computation time. Computation time (Equation 6) is primarily influenced by the attention blocks, predictors, and FFN blocks. The calculation involves dividing the computational workload of these components by the CPU flops (defined in Equation 7- 8). The flops of the selected CPU cores are specified in Equations 9.
\ 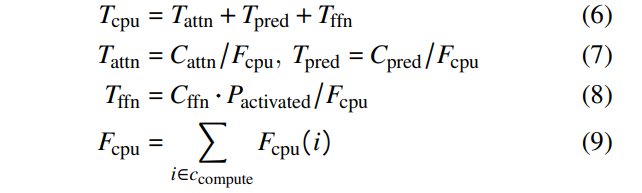
\ 
\ As FFN block computation overlaps with neuron loading, the planner must also account for I/O transmission time. This is calculated by dividing the volume of neurons transferred from flash storage (Equation 10) by the I/O bandwidth. This transferred volume depends on both the activation rate and the cache miss rate.
\ 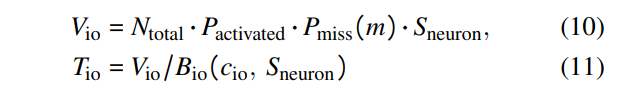
\ Finally, the planner calculates the time to load neurons from memory, which relates to the weight sizes of attention blocks, predictors, and neurons activated at runtime. The memory time is determined by dividing the total weight of activated neurons for one token by the memory bandwidth (Equation 11).
\
6 Implementation
PowerInfer-2 is developed on top of PowerInfer [30], a stateof-the-art serving framework designed for sparsely-activated LLMs, by integrating an additional 12K lines of C++ code into PowerInfer [30]. These enhancements encompass several key areas, including the polymorphic neuron engine, neuron cache, flexible neuron loading, and neuron-cluster-level I/O pipeline.
\ Since PowerInfer-2 depends on privileged system APIs (e.g., mlock that locks pages in memory) that needs the root permission, we built it on the Android [5] platform. Even though there is no need to alter the system kernel, a rooted Android system still provides us with considerable flexibility in developing and debugging our system. Furthermore, PowerInfer-2 is inherently designed with no modifications to the kernel, making it easily portable to other operating systems, including iOS [14] platform.
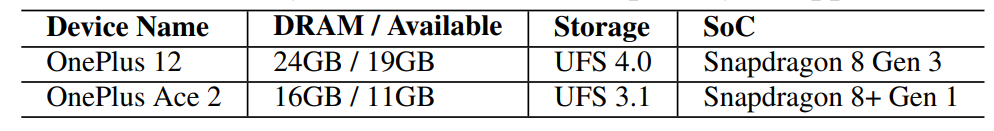
\ The current implementation of PowerInfer-2 supports a diverse array of LLMs with varying model sizes, including Llama-2 family [27] (7B, 13B), TurboSparse-Mistral [31] (7B), and TurboSparse-Mixtral [31] (47B).
\ 
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Zhenliang Xue, Co-first author from Institute of Parallel and Distributed Systems (IPADS), Shanghai Jiao Tong University;
(2) Yixin Song, Co-first author from Institute of Parallel and Distributed Systems (IPADS), Shanghai Jiao Tong University;
(3) Zeyu Mi, Institute of Parallel and Distributed Systems (IPADS), Shanghai Jiao Tong University ([email protected]);
(4) Le Chen, Institute of Parallel and Distributed Systems (IPADS), Shanghai Jiao Tong University;
(5) Yubin Xia, Institute of Parallel and Distributed Systems (IPADS), Shanghai Jiao Tong University;
(6) Haibo Chen, Institute of Parallel and Distributed Systems (IPADS), Shanghai Jiao Tong University.
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 license.
:::
\
You May Also Like

U.S. Moves Grip on Crypto Regulation Intensifies

The Stunning Crypto Winners For 2025 According To Top VCs
